In recent years, augmented reality (AR) has transitioned from being a futuristic concept to a practical tool with real-world applications. One of the most promising fields for AR technology is healthcare, where it is transforming patient care, medical training, and surgical procedures. As AR continues to evolve, its potential to enhance various aspects of healthcare becomes increasingly apparent. This article explores how augmented reality is reshaping the healthcare landscape, its benefits, and the challenges it faces.
1. What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) refers to the technology that overlays digital information—such as images, sounds, or data—onto the real world. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates an entirely artificial environment, AR enhances the real world by adding interactive elements. This is achieved through devices like AR glasses, smartphones, or tablets, which use cameras and sensors to integrate digital content with the user’s physical surroundings.
2. Applications of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality is making significant inroads into healthcare, with a variety of applications that improve both patient outcomes and medical training:
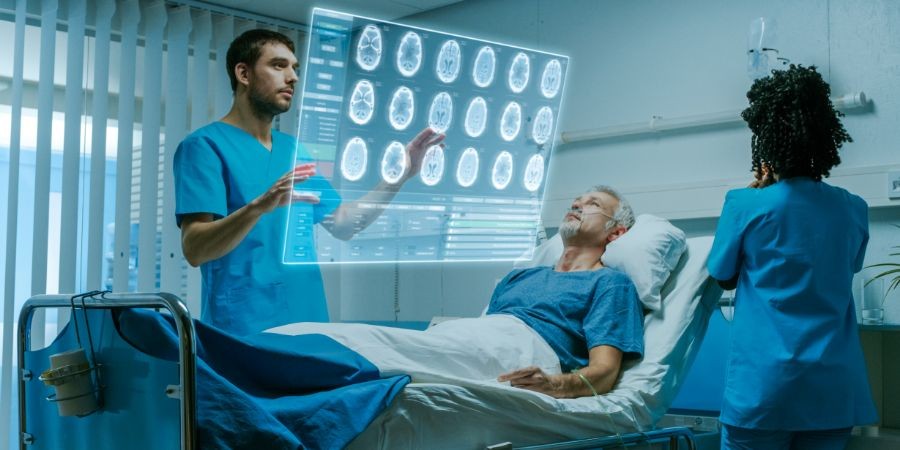
- Surgical Planning and Navigation: Surgeons can use AR to visualize complex anatomical structures during procedures. By overlaying 3D images of a patient’s organs and tissues onto their body, AR provides real-time guidance, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of errors. This capability is especially useful in complex surgeries, such as those involving tumors or intricate vascular systems.
- Medical Training and Education: AR offers immersive training experiences for medical students and professionals. Through AR simulations, learners can interact with 3D models of human anatomy, practice surgical techniques, and gain hands-on experience without the need for cadavers. This interactive approach enhances understanding and retention of medical knowledge.
- Patient Education and Engagement: AR can help patients better understand their conditions and treatment options. By using AR apps, patients can visualize their anatomy, see how medical procedures are performed, and explore potential outcomes. This increased understanding can lead to better patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: AR-based rehabilitation programs provide interactive and engaging exercises for patients undergoing physical therapy. By incorporating game-like elements and real-time feedback, AR can motivate patients and enhance their rehabilitation experience, leading to improved outcomes.
- Remote Assistance and Collaboration: AR facilitates remote consultations between healthcare professionals and experts. Through AR devices, specialists can provide real-time guidance and support during procedures or diagnostics, even if they are located miles away. This capability enhances collaboration and access to expertise in underserved areas.
3. Benefits of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The integration of AR technology into healthcare offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Accuracy and Precision: AR provides detailed, real-time visualizations of anatomical structures, enabling more accurate and precise medical procedures. Surgeons can plan and execute complex operations with greater confidence, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Improved Learning and Skill Development: AR simulations offer medical professionals an effective way to practice and refine their skills. The interactive nature of AR training enhances learning experiences, allowing users to gain practical knowledge and experience in a controlled environment.
- Increased Patient Understanding and Satisfaction: By visualizing their conditions and treatments through AR, patients can gain a clearer understanding of their health. This improved comprehension can lead to increased patient satisfaction and engagement in their care.
- Enhanced Accessibility: AR technology can bridge gaps in healthcare access by providing remote support and guidance. Specialists can assist with procedures or diagnostics from a distance, making high-quality care more accessible to patients in remote or underserved areas.
4. Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, the adoption of AR in healthcare faces several challenges:
- Cost and Accessibility: Implementing AR technology can be expensive, and not all healthcare facilities may have the resources to invest in these advanced tools. The cost of AR devices and software, as well as the need for specialized training, can be barriers to widespread adoption.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating AR technology with existing healthcare systems and workflows can be complex. Ensuring compatibility and seamless operation with electronic health records (EHRs) and other medical technologies is essential for successful implementation.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AR in healthcare involves handling sensitive patient data. Ensuring the security and privacy of this data is crucial, and healthcare providers must implement robust measures to protect patient information from unauthorized access.
- Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: AR applications in healthcare must comply with regulatory standards and ethical guidelines. Ensuring that AR technologies meet safety and efficacy requirements is important for maintaining patient trust and ensuring the quality of care.
5. The Future of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The future of AR in healthcare is promising, with several developments on the horizon:
- Advancements in AR Technology: Continued advancements in AR hardware and software will enhance the capabilities and applications of AR in healthcare. Improved device ergonomics, higher-resolution displays, and more intuitive interfaces will contribute to better user experiences.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: Combining AR with artificial intelligence (AI) can further enhance its capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze AR data, provide real-time insights, and assist in decision-making, leading to more precise and personalized healthcare solutions.
- Expansion of Applications: As AR technology evolves, its applications in healthcare are likely to expand. New use cases, such as AR-guided diagnostics, personalized treatment planning, and advanced rehabilitation programs, will continue to emerge, offering additional benefits to patients and healthcare professionals.
- Increased Adoption and Accessibility: As the technology matures and becomes more affordable, AR is expected to see increased adoption across healthcare settings. Greater accessibility and widespread use of AR tools will contribute to improved patient care and medical training.
Conclusion
Augmented reality is poised to transform the healthcare landscape by enhancing surgical precision, improving medical training, and empowering patients with greater understanding and engagement. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in AR technology promise a future where healthcare is more accurate, efficient, and accessible. By embracing AR, the healthcare industry can unlock new possibilities and drive innovation in patient care and medical education.